What is fire, a considerable amount of energy is released during combustion in the form of heat, flame, and other visible light as a result of the chemical reaction or series of chemical reactions in which fuel chemically reacts with an oxidizing agent

What is Fire Triangle Definition?
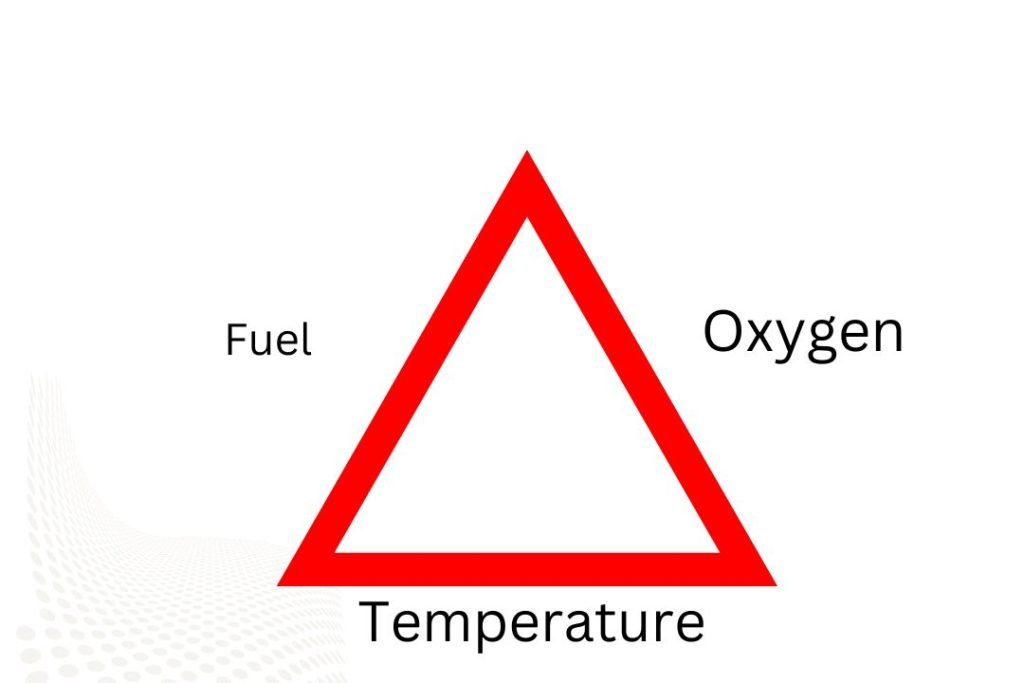
The “fire triangle” is a term used frequently to describe oxygen, heat, and fuel. There is actually a fire when the chemical reaction, the fourth element, is added.
Fire Triangle Components
According to the law of the triangle of combustion, a fire must have the following three elements in order to start. These three elements are called fire triangle components.
- 1 Fuel
- Oxygen or any other oxidizing agent
- 3 Heat
The Chain Reaction
Burning is the rapid oxidation of millions of vapor molecules. Energy is released during this process as heat and light, which is pure energy or radiant heat.
Since radiant heat radiates or travels in all directions, some of it returns to the source of fire or the fuel being burned.
It is termed radiation feedback. Air is attracted toward the region where the flame and vapor contact at the same moment.
The newly created vapor then starts to burn as a result. The chain reaction is set off as the flame grows. Fire spreads as long as there is ample fuel available.
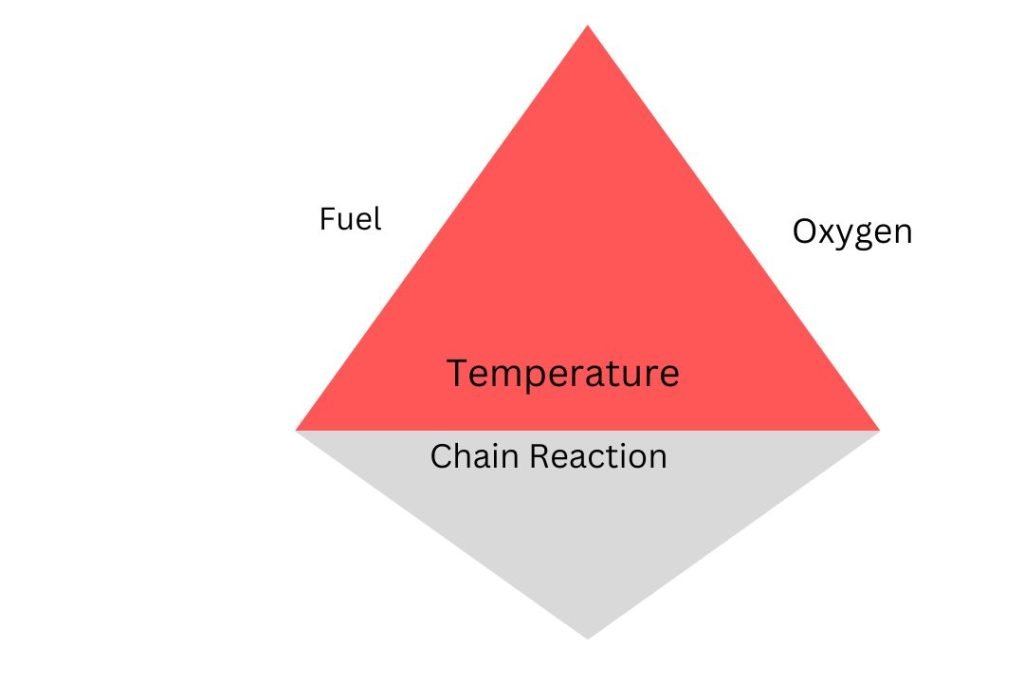
The Fire Tetrahedron
The fire triangle is a relatively simple way to explain the presence of any fire. However, it excludes the cascading effect of chemical reactions between fuel, oxygen, and heat. A more accurate illustration of the combustion process is the fire tetrahedron.
A tetrahedron is a solid having four triangle faces; if a chain reaction serves as its base, the faces that make up the other three are fuel, oxygen, and heat. The base holds up the other faces, symbolizing how a chain reaction might support combustion.
What is the Product of Fire?
Combustion is a chemical reaction between fuel and oxygen at a suitable temperature as a result of which heat, flame, and light are produced. In addition to these factors, there are so many products appeared as a result of the fire. Four of them are very important.
- Smoke
- Toxic gases
- Heat
- Flame
Smoke
The Smoke is a result of incomplete combustion if the three elements of combustion e.g. fuel, oxygen, and heat are in proper proportion, complete combustion takes place but if a reaction takes place at a lesser temperature compared to the fuel or oxygen and incomplete combustion take place and the result is, the release of unburnt carbon particles turned as smoke.

Effects of Smoke
Smoke is a major cause of fire spread.
The presence of smoke creates less visibility.
Inhalation can cause severe injuries.
It includes invisible poisonous gases which become a major killer (50% to 75% of deaths) in fire incidents.
Smoke irritation in the eyes and lungs frequently causes panic conditions
Types of Smoke
- Wooden smoke (unburned carbon particles).
- Metallic smoke (unburned metal or particles).
- Chemical smoke (unburned particles of chemical).
- Cigarette smoke (nicotine particles).
Toxic Gases
Combustible materials are usually based on complicated organic as well as inorganic substances, so toxic gases are produced during the combustion process.
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Sulfur monoxide
- Hydrogen cyanide
- Ammonia etc.
Heat
Heat is also generated in the chemical reaction and has its own effects:
- Further propagation of fire.
- Burns caused the firefighter.
Flame
Flame, a result of combustion, produces special risks like:
- Fire due to direct contact with flame
- Emits light
- Release of sufficient heat.
- Burns caused the firefighter.
Ash
Ash is a product that cannot ignite or further propagate the fire
Light
Light is the last product of fire which is generated by its ignition of it.
Physical Properties of Matter
Atom
The smallest unit of an element, having all the characteristics of that element and consisting of a dense, central, positively charged nucleus surrounded by a system of electrons.
Molecule
The smallest particle of a substance that retains the chemical and physical properties of the substance and is composed of two or more atoms; a group of like or different atoms held together by chemical forces.
Inter Molecular Forces
The force between two molecules; is the attractive force that holds two molecules together.
Intra-molecular forces are forces within a molecule (i.e., between atoms in the molecule).
States of Matter
The matter is made up of atoms and molecules. Matter exists in three states:
- Solid
- Liquid
- Gas
Some knowledge about these states is helpful in understanding fire behavior.
Solid
A solid does not flow under stress, instead, it has a definite capacity for resisting forces and ordinary conditions retain a definite shape and size.
Liquid
A nongaseous substance is composed of molecules that move and flow freely and assumes the shape of the container that holds it.
Gas
Division of Matter on The Basis of Conductivity
The matter can be divided into three groups
- Conductor
- Nonconductor or insulator
- Semiconductor
Conductor
- A material through which electric current can pass is a good conductor. Copper or aluminum is normally used to conduct electricity in commercial and household systems.
OR
- A substance or medium that conducts heat, light, sound, or especially an electric charge.
Semi-Conductor
Any of various solid crystalline substances, such as germanium or silicon, have electrical conductivity greater than insulators but less than good conductors and are used especially as a base material for computer chips and other electronic devices.
A materials product – usually comprised of silicon – which conducts electricity more than an insulator but less than a pure conductor, such as copper and aluminum. Semiconductors are usually very small and complex devices and can be found in thousands of products such as computers, cell phones, appliances, and medical equipment.
Non Conductor Or Insulator
- A material that does not easily transmit energy, such as electric current or heat. Materials such as wood, plastic, and ceramics are insulators. Fiberglass is an example of a heat insulator.
- Anything that slows or stops the flow of electricity, heat, or sound.
Spread of Fire
The spread of fire is a composition of a large number of products and the major product is the release of heat (thermal waves) in all directions. Heat is a form of energy and energy travels from one body to the other bodies in three possible ways which are:
- Conduction
- Convection
- Radiation
Conduction
Conduction is the process of transferring heat in which, Heat transfers in the matter (Solids) by the movement of the kinetic energy from one particle to another.
Heat energy transfer directly from one molecule to another, much as a billiard ball transfer energy from one ball to the next.
Metals generally have a greater ability to conduct heat energy than wood.
Materials that are good conduction are rarely the primary means of spreading a fire.

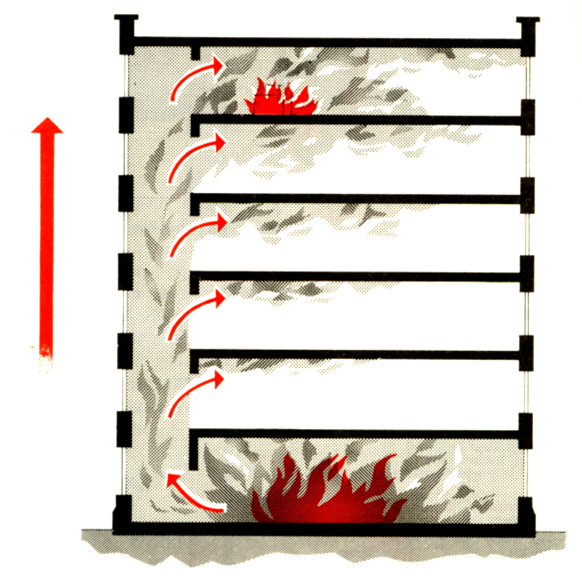
Convection
It occurs in liquids and gases.
It is the circulatory movement that occurs in a gas or liquid.
The convection currents in a fire involve gases that are generated by the smoke.
The heat of the fire warms the gases and particles in the smoke
The pattern of convection in a building or a room generally starts from the floor of the building and travels along the ceiling.
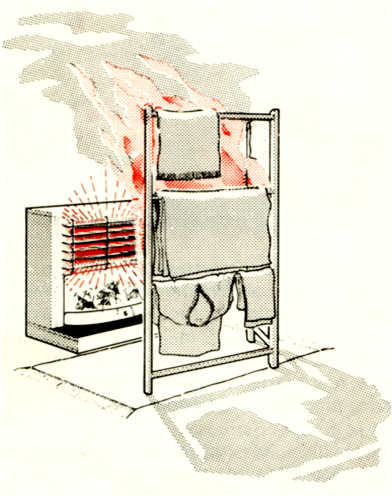
Radiation
It does not require any medium to transfer the heat energy.
In radiation the heat transfers through the emission of energy in the form of invisible waves.
It has no specific direction and can travel in all the directions
In Thermal Radiation heat travels in all directions and the effect of thermal radiation can’t be seen or felt until the radiation strikes an object and heats the surface of the object.
Principles of Fire Fighting
Introduction
Fire is a very complicated and technical subject. So the experts have devised the following basic principles to extinguish the fire.
- Starvation.
- Smothering.
- Cooling.
- Break down of chain reaction
Starvation
According to this strategy, the fire is starved of fuel. Various methods can be used to achieve this so
the gas fires are an example of cutting off the fuel supply. Diluting the burning liquid fuel with water or another solvent is another (alcohol fires).
The introduction of some inert materials, which will reduce the fuel concentration in the flammable fuel-air mixture, such as Nitrogen and Co2, will lower the fuel concentration in the various production zones.
Smothering
In this technique, the supply of oxygen or any oxidizing agent required for combustion is checked and in the absence of an oxidizing agent. The Combustion reaction cannot prolong, so the fire is extinguished.
Cooling
As a general rule, if a temperature is dropped combustion can start and continue therefore a constant supply of heat energy is necessary to produce and sustain the combustion process.
This heat energy is utilized to maintain the desired level of temperature. This can be done in firefighting by doing the following.
Using Water
Water applied in any form absorbs heat from the combustion zone, thus lowering the temperature and the result is the extinguishment of the fire.
Foams
Because foams are often made of water and the water content is depleted by the heat absorption from the combustion zone, which lowers the temperature.
Use of All Types of Extinguishing Agents
When used on a fire, all extinguishers are deployed under pressure and any substance that is deployed under pressure absorbs heat.
Break Down of Chain Reaction
In this method, the radiation feedback to the seat of the fire is inhibited or stopped by using different extinguishing materials like dry chemical powder and dry powder, etc.
Conclusion
In this article, I will discuss fire definition, chemistry, the triangle, the component of the fire triangle, and how to extinguish it. Describe the properties of matter and how the fire is spread. I discuss the principles of firefighting.
For more detail about the blog visit Fr Safety solutions.



